引入
- How application-specific Data
- Flows through the
- Nodes (BBs/statements) and
- Edges (control flows) of
- CFG (a program)?
- Flows through the
Over-approximation (Safe-approximation)
- may analysis: safe=over
- outputs information that may be true (over-approximation)
- must analysis: safe=under
- outputs information that must be true (under-approximation)
Over- and under-approximations are both for safety of analysis
基本概念
输入输出状态
- 每一条IR语句将一个输入状态转变为一个新的输出状态
- 每个(输入输出)状态都与一条语句之前/之后的**程序点(Program Point)**关联
- 例如s1→s2,则
OUT[s1]与IN[s2]为同一个程序点 - s1→s2←s3,则
- : meet符号
OUT[s1]和OUT[s3]代表各自的出口,但IN[s2]代表汇聚后,进s2前的状态
- 例如s1→s2,则
什么是数据流分析:
- 在每个数据流分析的应用中,我们将每一个程序点与一个数据流值关联,这个值代表那一个点的程序状态的例子。
- 给程序中所有语句的IN和OUT找到一个solution(关联一个data-flow value),基于转换函数和控制流的safe-approximation约束规则
约束的符号
Transfer Function
- Forward Analysis
- Backward Analysis
Control Flow
- 基本块里的Control flow
- 基本块之间的Control flow
- 顺序的时候
- 汇聚的时候
Reaching Definitions
在程序点p定义的v在达到程序点q的路径上,没有被覆盖掉
案例:在CFG开头加一堆dummy definition,如果能reach到使用变量的点,说明有变量未初始化的错误。只要有一条路径能reach到就报错,所以是may analysis
-
Transfer Function
-
Control Flow
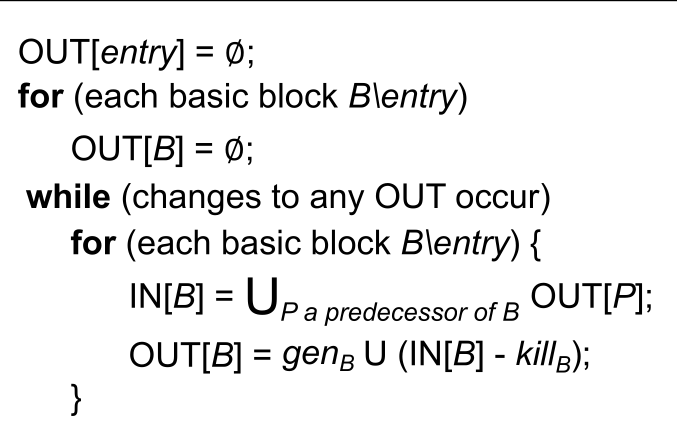
Algorithm of Reaching Definitions Analysis
��LINPUT: CFG ( and computed for each basic block )
OUTPUT: and for each basic block
METHOD:
OUT[entry] = ∅;
for (each basic block B except entry)
OUT[B] = ∅;
while (changes to any OUT occur)
for (each basic block B except entry) {
IN[B] = Union of OUT[P] for all P that are predecessors of B;
OUT[B] = gen_B U (IN[B] - kill_B);
}
Live Variables Analysis
判断变量v在程序点p处的值后续是否被使用(至少一条路径中)。
案例:分配寄存器,仍有机会被使用的值(尽量)不会被移出寄存器
从后往前分析
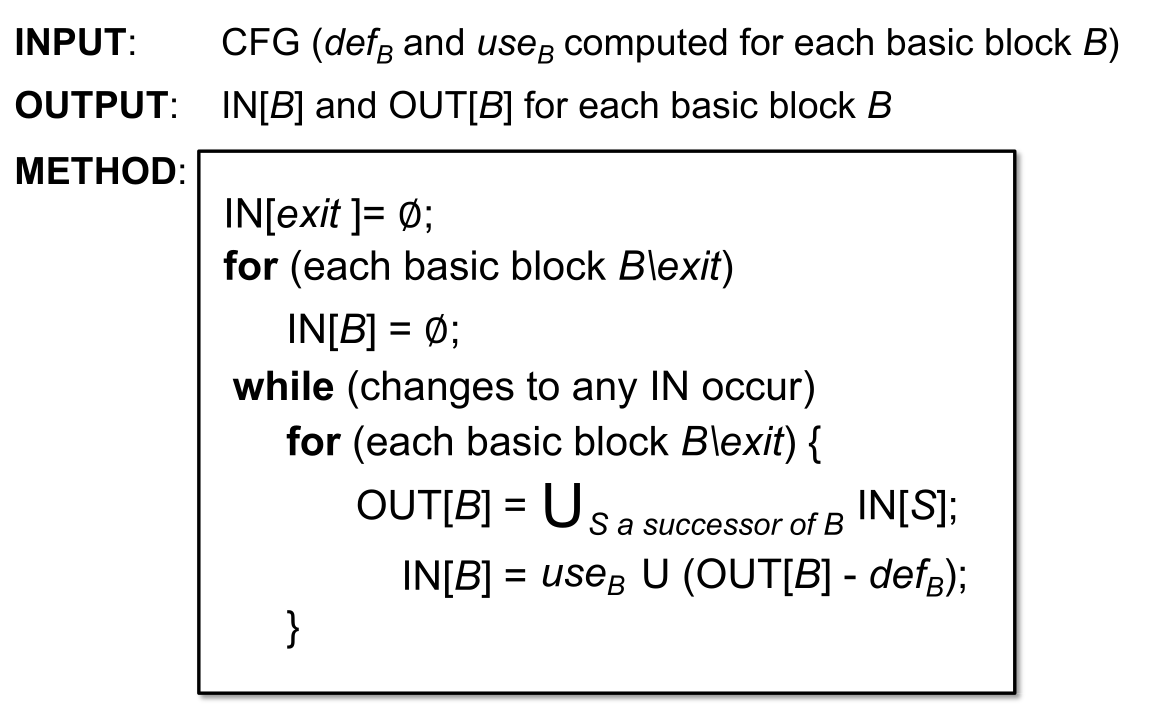
Algorithm of Live Variables Analysis
INPUT: CFG (def_B and use_B computed for each basic block B)
OUTPUT: IN[B] and OUT[B] for each basic block B
METHOD:
IN[exit] = {}
for (each basic block B except exit)
IN[B] = {}
while (changes to any IN occur)
for (each basic block B except exit) {
OUT[B] = Union of IN[S] for S a successor of B
IN[B] = use_B U (OUT[B] - def_B)
}
Available Expressions Analysis
到p点所有的路径中,都对表达式x op y求过值,且(每条路径)最后一次使用后,x和y的值没有被覆盖。
这样在p点使用该表达式时,就可以重复利用之前的值了
这个是Must analysis
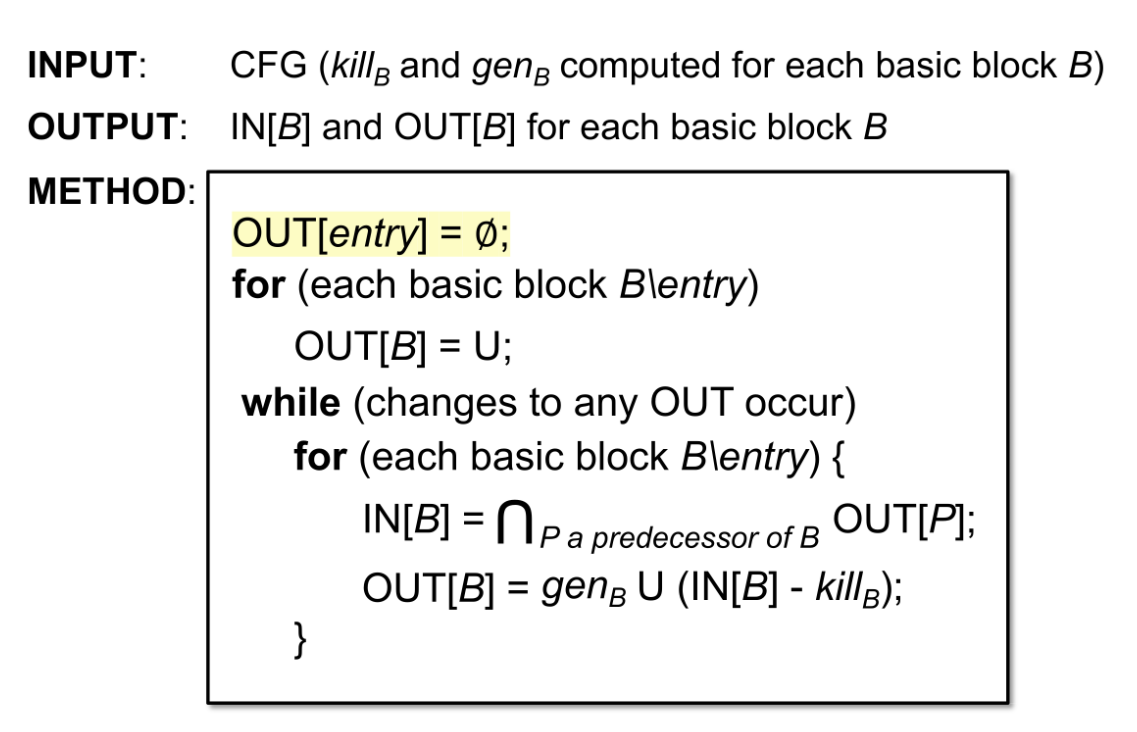
Algorithm of Available Expressions Analysis
INPUT: CFG ( and computed for each basic block )
OUTPUT: IN[] and OUT[] for each basic block
METHOD:
OUT[entry] = ∅;
for (each basic block B \ entry)
OUT[B] = U;
while (changes to any OUT occur)
for (each basic block B \ entry) {
IN[B] = ∩ { OUT[P] | P is a predecessor of B };
OUT[B] = gen_B ∪ (IN[B] - kill_B);
}
Analysis Comparison
| Reaching Definitions | Live Variables | Available Expressions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | Set of definitions | Set of variables | Set of expressions |
| Direction | Forwards | Backwards | Forwards |
| May/Must | May | May | Must |
| Boundary | OUT[entry] = ∅ | IN[exit] = ∅ | OUT[entry] = ∅ |
| Initialization | OUT[B] = ∅ | IN[B] = ∅ | OUT[B] = U |
| Transfer function | OUT/IN = gen ∪ (IN/OUT - kill) | ||
| Meet | ∪ | ∪ | ∩ |